WHAT'S NEW IN TUBERCULOSIS
Monday, 12 November 2007
South African scientists crack drug-resistant TB code
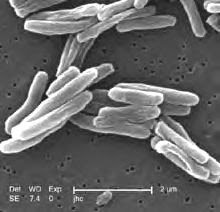
South African scientists have sequenced the entire genome of a strain of extremely drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (XDR-TB).
Scientists from the Nelson R. Mandela School of Medicine at the University of KwaZulu Natal, and the National Genomics Platform sequenced the genome 20 times to distinguish mutations from sequencing errors and provide a reference for further sequencing projects of XDR and multidrug-resistant TB. Lifelab, a funding mechanism of the South African Department of Science and Technology, funded the sequencing initiative. The cost of the research has not been disclosed.
James Sakwa, manager of the National Genomics Platform, told SciDev.Net that the next step will be to to develop a diagnostic kit that can quickly and efficiently diagnose this strain of XDR-TB. The breakthrough was achieved by using "pyro-sequencing" technology, where massive amounts of information are produced in parallel.
"This enabled us to sequence the whole genome within a week," he said. If the scientists had used older technologies, it would have taken about a year to achieve the same result.Proposals for the sequencing of other TB strains are currently being considered by the National Genomics Platform. "The truth is we don't know how many mutations of XDR TB there are," Sakwa said.The findings were announced at a press conference in Durban, KwaZulu Natal province, South Africa in October.
http://tinyurl.com/345l8g
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment